Agile 102 Workshop Syllabus: Difference between revisions
| Line 166: | Line 166: | ||
!Learning Objectives | !Learning Objectives | ||
!Concept Centre | !Concept Centre | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Agile Manifesto]] | |[[Agile Manifesto]] | ||
| Line 206: | Line 186: | ||
* [[Prioritisation Exercise]] | * [[Prioritisation Exercise]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |Batch size and Flow | ||
| | | | ||
* Limiting the work in progress | * Limiting the work in progress | ||
* Working with constraints | * Working with constraints | ||
| | | | ||
* [[The Dice Game]] | * [[The Dice Game]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 219: | Line 197: | ||
* Generating impact with iterations | * Generating impact with iterations | ||
* Capacity planning | * Capacity planning | ||
| | | | ||
* [[Prioritisation Exercise]] | * [[Prioritisation Exercise]] | ||
| Line 235: | Line 207: | ||
| | | | ||
* [[Daily Scrum From Heaven]] | * [[Daily Scrum From Heaven]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Agile Estimation|Agile Estimation]] | |[[Agile Estimation|Agile Estimation]] | ||
Revision as of 04:13, 23 May 2022
After the practical exercise in the Agile 101 Workshop, this workshop focuses on developing teams' ability to apply some of their experiences to another simulation project, which needs a next level understanding of the Agile concepts.
This workshop sees teams selecting a project, developing an estimated and prioritised backlog of work, running a dice based simulation against it and making critical decisions to deliver the most value within the time and cost constraints.
Materials
- Large poster illustrating the Agile framework for the session such as Scrum for example
- Flip chart paper and markers
- Post-it notes and markers
- A4 spare paper
- Dice, enough for pairs of attendees to be able to throw up to 3 dice
- Release and Sprint burn down charts
- Visible timer to indicate the time left for the activities
- Music playlist and sound system to help play low level music whilst the teams are working
- Debrief Cards
Setup
The setup for the room with up to 16 participants includes:
- Concept centres for each activity on offer (including a poster, instructions, materials and equipment)
- Large poster of the Agile framework to be used visible on the wall
- Several workstations arranged in cafe seating available for multiple table groups
Team Workstations
Each team should have setup:
- Poster of their team name and sense of identity
- Flip chart paper for their Backlog or Product Backlog of work
- Flip chart paper for their Iteration or Sprint Backlog
- Agile 102 Instructions
- Table where to work
Timings & Run Sheet
Provide 3 hours for teams to orientate themselves to their project, conduct 4 iterations or Sprints and conclude with a reflection:
- Introduction and orientation of the approach - 15 mins
- Team self selection
- Team name poster and workstation setup
- Run through of the Agile framework poster and how the session is going to run
- 4 x iterations or Sprints - 150 mins:
- Sprint Planning (if using Scrum) - Team decides how long
- Sprint or iteration to do the chosen activities - 25 mins - Including Sprint Planning time (if used)
- Group Sprint Review as a Feature Fair to enable teams to interact, offer feedback and discuss what they have learned - 5 mins
- Sprint Retrospective or other reflection for the teams to improve how they do things - 5 mins
- Overall share back and reflection on the workshop with Debrief Cards if needed - 15 mins
Total: 3 hours
Activity Instructions
Part 1: Release Planning
- Each team choose a desired scenario
- As a team review the scenario and the associated user journey
- Draw up sketches of the outcome using Crazy 8s Sketching
- Using dots or similar review the sketches and form a feature heatmap of the best features to include
- Draw a composite sketch of the best features
- Arrange the sketches and the user journey in the order of time as a horizontal row
- Brainstorm epics from the user journey and sketches to form the "back bone" of a Story Map
- Decompose the epics into stories or tasks as the "ribs" of the story map
- Using Kano Analysis categorise the stories or tasks
- Estimate the stories or tasks using Affinity Mapping
- Re-form the story map into iterations with a goal for each iteration
- Add post-it notes down one side of the Story Map indicating Sprints 1-5 to form swim lanes for each of the Sprints
- Adjust the iterations between the Sprint swim lanes to form a release plan over the 5 Sprints
- Call over the facilitator to review and discuss
Part 2: Simulation
- As a team sum up the total number of story points for all of the items in the Product Backlog
- Divide the total number of story points on the Product Backlog by 150. This is the number of dice to now request from the facilitator.
- On the Release Burndown chart mark off the total number of story points on the vertical axis, and calculate the divisions on the vertical axis. (For example, if my total number of story points on my Product Backlog is 100, then I will put 100 on the top of the vertical axis and mark off 10 story points for each division on the vertical axis.)
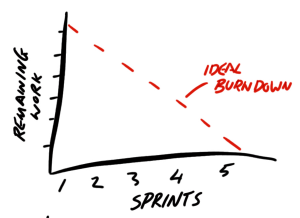
- Finally, draw the ideal burn down line from the total number of story points on the vertical axis to Sprint 5 on the horizontal axis. (This should provide a diagonal line from the total amount of work down to zero by Sprint 5.)
- Repeat steps 1, 3 and 4 for the Sprint 1 Burndown chart, but this time only for the items in Sprint 1 on the Product Backlog. (The end result should be a total number of story points for Sprint 1 on the vertical axis, the vertical axis divided into equal divisions, and a diagonal line from the top of the vertical axis to day 5 on the horizontal axis.)
- DO NOT GO BEYOND SPRINT 1 at this point
- Working on Sprint 1, throw the dice. The total numbers from the dice throw now represent the work that was completed on day 1.
- On the Sprint 1 Burndown Chart decrement the dice throw (work done) for day 1 from the total number of story points and mark how much work is remaining on the chart for day 1.
- Repeat step 7 and 8 for each of the remaining 4 days for Sprint 1. (If the burndown chart shows that the work is completing ahead of time, bring in an additional item into Sprint 1 on the Product Backlog and mark off how much work is remaining with the new item.)
- The first Sprint has now been completed.
- Next update the Velocity chart with the total work completed for Sprint 1. (This should be around half way up the vertical axis, as future Sprints may deliver more or less work.)
- Going back to the Release Burndown chart, decrement the work done for Sprint 1 from the total amount of work and mark how much total work is remaining on the chart after Sprint 1.
- On the Product Backlog mark off the items that were completed during Sprint 1 as “Done” with a bold tick or similar.
- Performing a Sprint Review adjust the release plan on the Product Backlog by rearranging the work planned for the future Sprints based upon the velocity. (Any items not completed in Sprint 1 should now be moved to a future Sprint.)
- Repeat steps 5 – 14 for the remainder of the Sprints and adjusting the Product Backlog as you go to provide the best possible value with respect to the velocity.
- Call over the facilitator for review and discussion.
Concept Centres
Syllabus
Workshop Format
Here is a table of the learning outcomes from the workshop format and how it is to be run:
| Topic | Learning Objectives | Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Team Definition |
|
|
| Agile Framework | ||
| Agile Roles |
|
|
| Sprints, Iterations and Flow |
|
|
| Sprint Planning / Iteration Planning |
|
|
| Product Backlog Refinement |
|
|
| Sprint Review / Iteration Review |
|
|
| Sprint Retrospective / Kaizen |
|
|
Concept Centres
Here is a table of suggested concept centres mapped to the intended learning outcomes that can be used for teams to choose from as activities to be done during their sprints:
| Topic | Learning Objectives | Concept Centre |
|---|---|---|
| Agile Manifesto |
|
|
| Traditional vs Empirical control methods |
|
|
| Iterative vs. Incremental delivery |
|
|
| Batch size and Flow |
|
|
| Iteration Planning |
|
|
| Daily Scrum / Daily Standups |
|
|
| Agile Estimation |
|
See Also
- Agile 101 Workshop Syllabus
- Scrum Framework
- Kanban Framework
- Scrum Master Coaching Syllabus
- Product Owner Coaching Syllabus
References
- Scrum Foundations Learning Objectives, accessed 21 Jan 2019