Release Strategy: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Agile:Articles]][[Category:Agile]] | [[Category:Agile:Articles]][[Category:Agile]] | ||
== | ==Delivery Focus== | ||
Teams that only consider a superficial understanding of the work tend to adopt a | Teams that only consider a superficial understanding of the work tend to adopt a reactionary '''conveyor belt''' style of working that orders the Product Backlog and then progressively works through each of the items in order without too much thought about why it is needed or any sense of adaptation. They drop into a "delivery focus" where the deadline and the number of items delivered becomes more important than what '''value''' is being delivered to the customer. The metrics and efficient delivery becomes more important than the value delivered. | ||
There also seems to be an underlying assumption that all items are of equal value, and that more incremental delivery of items equals more value delivered. Which is not necessarily the case. More value delivered is more value delivered. | |||
==Value Focus== | |||
Teams that have more customer awareness tend to focus on the value of items and how to deliver that value. They will explore, prototype and seek feedback to see what resonates with customers throughout the delivery of the work, and actively adapt what they are doing accordingly. Here there is also a tendency to accept that not all items on the backlog are equal and that some items are more valuable than others, which presents opportunities and options to exploit. More emphasis and effort may be placed on higher value items, and lower emphasis and effort on lower value items. | |||
Additionally, teams with high value focus will not look to deliver the whole backlog of items, but will instead look to maximise the value from the backlog. When the backlog ceases to yield sufficient value in the eyes of the customer, then they will look to move on to another body of work. Hence, not all of the items on the backlog may be worked on, which can be quite sobering for delivery focused teams. | |||
'''Value''' is also subjective and socially created, which also means that perceived value can change over time. This then prompts teams to continually test their assumptions with customers throughout the work to understand where they are adding value, and where the highest yield of value is on the backlog, which they accept is not a static quality and may change and migrate. | |||
==Risk Focus== | |||
Some bodies of work present key risks, such as, integration risk for a central framework that needs to connect to several services for example, or a new app that has a volatile value proposition in the eyes of the customer. Teams with a good awareness of the key risks in the body of their work will tend to address those risks head on in the early iterations. Neutralising the risks early then takes the anxiety out of the work and the team can then focus on how to make the product better with each successive iteration. | |||
For the example with the central framework, the integration risk may be neutralised straight away using a '''steel thread''' [[Backlog Strategy Archetypes|Backlog Strategy Archetype]] that looks to connect each of the services together from the outset of the work using a simple '''ping''' for example. Here the integration risk has been neutralised straight away and now the team can focus on adding value on top of this rudimentary connection in successive iterations. | |||
The value proposition example may involve initially prototyping multiple approaches for the apps and getting out their and interacting with potential customers to see what resonates and what doesn't. The initial investment to prototype then furnishes the team with more knowledge about what will resonate and what does not, helping them to refine their backlog and adapt their approaches accordingly. | |||
==Exploration Focus== | |||
Teams that are not sure of what the problem is let alone what the solution is, may respond to this situation with successive prototypes to learn about problem space and the solution space. Working closely with customers and stakeholders to continually refine their prototypes and narrow down where the value proposition is with regards the problem to solve, and the solution to solve it. | |||
A backlog of work may well invest initially in prototyping with a view to converging and narrowing the scope to what the problem really is and a valuable solution for it in later iterations. | |||
==Multi Release Strategies== | ==Multi Release Strategies== | ||
When working with multiple releases it is always good to consider whether you are releasing to earn or releasing to learn. The latter implying a rapid release cycle to actively foster and then respond to feedback. | When working with multiple releases it is always good to consider whether you are '''releasing to earn''' or '''releasing to learn'''. The latter implying a rapid release cycle to actively foster and then respond to feedback. | ||
Organisations that are used to infrequent and large releases tend to defend their approach by citing risk concerns and that releasing less often reduces the risk. As a result, the releases tend to be large, cumbersome and often too complex to provide any degree of risk mitigation. | Organisations that are used to infrequent and large releases tend to defend their approach by citing risk concerns and that releasing less often reduces the risk. As a result, the releases tend to be large, cumbersome and often too complex to provide any degree of risk mitigation. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 41: | ||
===Minimum Marketable Product (MMP)=== | ===Minimum Marketable Product (MMP)=== | ||
This is also a multi release strategy with the prime focus being on the ability to learn from customers and end users, testing assumptions and the market with an idea. The feedback translates into hypotheses for future releases and navigates the product towards the customer desires. | This is also a multi release strategy with the prime focus being on the ability to learn from customers and end users, testing assumptions and the market with an idea. The feedback translates into hypotheses for future releases and navigates the product towards the customer desires. | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
Revision as of 01:02, 27 October 2022
Delivery Focus
Teams that only consider a superficial understanding of the work tend to adopt a reactionary conveyor belt style of working that orders the Product Backlog and then progressively works through each of the items in order without too much thought about why it is needed or any sense of adaptation. They drop into a "delivery focus" where the deadline and the number of items delivered becomes more important than what value is being delivered to the customer. The metrics and efficient delivery becomes more important than the value delivered.
There also seems to be an underlying assumption that all items are of equal value, and that more incremental delivery of items equals more value delivered. Which is not necessarily the case. More value delivered is more value delivered.
Value Focus
Teams that have more customer awareness tend to focus on the value of items and how to deliver that value. They will explore, prototype and seek feedback to see what resonates with customers throughout the delivery of the work, and actively adapt what they are doing accordingly. Here there is also a tendency to accept that not all items on the backlog are equal and that some items are more valuable than others, which presents opportunities and options to exploit. More emphasis and effort may be placed on higher value items, and lower emphasis and effort on lower value items.
Additionally, teams with high value focus will not look to deliver the whole backlog of items, but will instead look to maximise the value from the backlog. When the backlog ceases to yield sufficient value in the eyes of the customer, then they will look to move on to another body of work. Hence, not all of the items on the backlog may be worked on, which can be quite sobering for delivery focused teams.
Value is also subjective and socially created, which also means that perceived value can change over time. This then prompts teams to continually test their assumptions with customers throughout the work to understand where they are adding value, and where the highest yield of value is on the backlog, which they accept is not a static quality and may change and migrate.
Risk Focus
Some bodies of work present key risks, such as, integration risk for a central framework that needs to connect to several services for example, or a new app that has a volatile value proposition in the eyes of the customer. Teams with a good awareness of the key risks in the body of their work will tend to address those risks head on in the early iterations. Neutralising the risks early then takes the anxiety out of the work and the team can then focus on how to make the product better with each successive iteration.
For the example with the central framework, the integration risk may be neutralised straight away using a steel thread Backlog Strategy Archetype that looks to connect each of the services together from the outset of the work using a simple ping for example. Here the integration risk has been neutralised straight away and now the team can focus on adding value on top of this rudimentary connection in successive iterations.
The value proposition example may involve initially prototyping multiple approaches for the apps and getting out their and interacting with potential customers to see what resonates and what doesn't. The initial investment to prototype then furnishes the team with more knowledge about what will resonate and what does not, helping them to refine their backlog and adapt their approaches accordingly.
Exploration Focus
Teams that are not sure of what the problem is let alone what the solution is, may respond to this situation with successive prototypes to learn about problem space and the solution space. Working closely with customers and stakeholders to continually refine their prototypes and narrow down where the value proposition is with regards the problem to solve, and the solution to solve it.
A backlog of work may well invest initially in prototyping with a view to converging and narrowing the scope to what the problem really is and a valuable solution for it in later iterations.
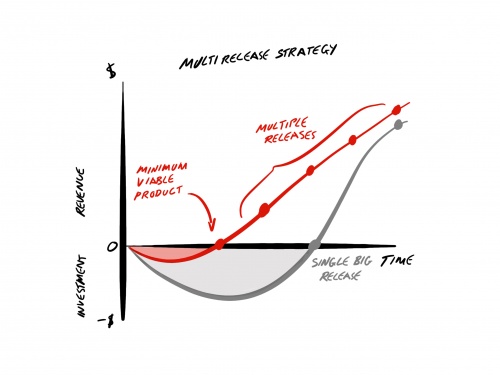
Multi Release Strategies
When working with multiple releases it is always good to consider whether you are releasing to earn or releasing to learn. The latter implying a rapid release cycle to actively foster and then respond to feedback.
Organisations that are used to infrequent and large releases tend to defend their approach by citing risk concerns and that releasing less often reduces the risk. As a result, the releases tend to be large, cumbersome and often too complex to provide any degree of risk mitigation.
Conversely, releasing more often with smaller releases provides a risk mitigation strategy of managing small amounts of risk more often. The releases are small, easily managed, less complex and we get more practice at releasing, which improves the probability of releasing even faster, especially if this can be automated.
Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Organisations that are in their infancy with Agile approaches and have traditionally worked with projects and large infrequent releases often misuse this approach and consider the MVP to be the basic release, or in the worst case, a substitute for the word “release”. Conversations often take place about what is in or out of the MVP, which when translated often means which items are in or out of the release.
MVP was always intended as a multi release strategy, with the intention being to provide something into the market quickly that isn’t necessarily going to earn any revenue or even customer loyalty, but the information and feedback gained can be invaluable for the next release in an evolutionary strategy. If some revenue can be earned whilst the project is still running then that can be used to offset the cost of development, which relieves the commercial pressure.
Minimum Marketable Product (MMP)
This is also a multi release strategy with the prime focus being on the ability to learn from customers and end users, testing assumptions and the market with an idea. The feedback translates into hypotheses for future releases and navigates the product towards the customer desires.